In manufacturing, delays in decision-making can mean defects, downtime, and lost revenue. That’s why manufacturers implement QRQC. Quick Response Quality Control, or QRQC, is a lean problem-solving method designed to catch and correct issues directly on the shop floor quickly.
Whether you call it lean manufacturing or just “how we solve problems,” QRQC can help you improve production quality. It can also boost team collaboration, and reduce waste. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to implement QRQC in your manufacturing plant.
What Is QRQC (Quick Response Quality Control)?
QRQC is a structured, real-time problem-solving method you can use to quickly detect, analyze, and fix production problems at their source. This prevents them from happening again.
Originally developed in the automotive industry, many industries have adopted the QRQC process for its speed and effectiveness. Its hands-on approach empowers frontline teams to take immediate action when problems come up, while still following a standard problem-solving process.
This method blends visual management, data-driven decision-making, and lean thinking. The result? Faster decisions, fewer disruptions, and a stronger culture of continuous improvement.
The QRQC Principles and Process
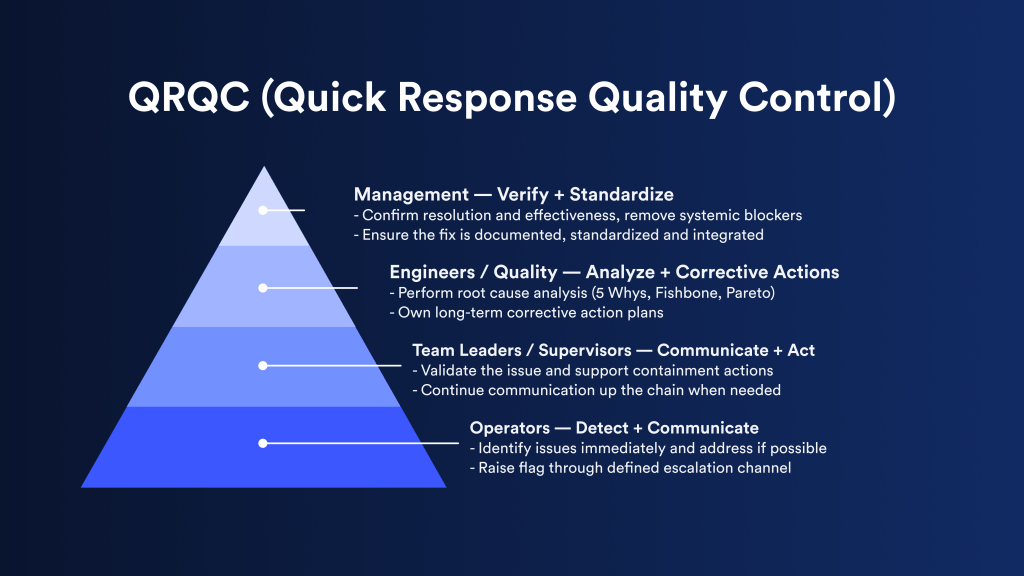
At its core, QRQC revolves around three key principles:
- Speed: Problems are addressed as soon as they’re identified, ideally within minutes and not hours. This real-time response minimizes downtime and prevents the issue from spreading across batches or shifts.
- Structure: A clear, repeatable process guides teams through each step of the problem-solving method. This structure ensures that everyone, from operators to managers, approaches problems the same way.
- Standardization: Capture information in a consistent format and share it across shifts, teams, and departments. This makes it easy to track recurring issues, share learnings, and maintain a culture of continuous improvement.
This method typically follows a series of key steps that provide a clear, structured approach and help drive continuous improvement across the organization.
The five key steps are:
- Detect: Spot the problem immediately on the line or at the workstation. Anyone can raise a flag, which empowers operators to take ownership of quality.
- Communicate: Escalate the issue to the appropriate person or team using predefined channels. The faster the right people are looped in, the faster a solution can be implemented.
- Analyze: Identify the root cause. Teams often use structured lean problem solving tools to dig deeper and avoid superficial fixes. This includes the 5 Whys, Pareto analysis, or the Ishikawa (Fishbone or Cause-and-Effect) diagram.
- Act: Apply short-term containment to minimize impact, then define and implement a long-term corrective action. Assign ownership and set deadlines.
- Verify: Check that the solution has resolved the issue and that it won’t reoccur. If necessary, update standard work instructions, training materials, or processes.
Why Manufacturers Choose QRQC
Whether you’re in aerospace, food and beverage, or pharmaceuticals, this method helps you solve problems faster and more effectively. It improves your factory’s responsiveness, boosts quality, and engages frontline teams in continuous improvement.
QRQC is simple to learn, easy to standardize, and scalable across departments. It is especially effective for immediate response and containment. For recurring or complex problems, teams can escalate to more in-depth approaches like the 8D Method or PDCA cycle.
It’s an ideal fit for manufacturers looking to reduce quality issues and streamline communication. Especially when paired with digital tools.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implement QRQC
Ready to bring QRQC to your factory floor? Follow these steps to ensure a smooth rollout:
1. Align Leadership
Before introducing any new process, leadership buy-in is essential. Make sure your plant managers, supervisors, and team leaders understand how it supports broader goals. These goals include improving manufacturing quality control and reducing downtime.
2. Choose a Pilot Area
Start small. Pick one production line, shift, or area to test this process. This controlled environment helps you iron out challenges before scaling.
3. Train Your Teams
Training is key. Operators, line leads, and support functions should all understand the process and their role in it. Focus on real-time problem detection, clear communication and escalation, and basic root cause analysis tools. Also, use visual management tools like SQDIP or A3s.
4. Implement Visual Management
Use a digital visual management solution to track issues. The problem-solving board should display active problems. It must list their status, who is responsible, timelines for resolution, and metrics related to quality and performance. This encourages accountability and transparency.
5. Define Escalation Protocols
When should a problem be escalated? Who needs to be involved? Clear escalation rules help avoid delays and keep decision-making close to the problem.
6. Reinforce Daily Discipline
This method thrives on consistency. Set a standard cadence for daily QRQC meetings, typically at the start of each shift. Use these to review issues, update statuses, and align on priorities.
7. Scale and Improve
Once your pilot is running smoothly, expand it across other areas. Encourage teams to share best practices and lessons learned.
Overcome 3 Common Challenges of QRQC
QRQC is powerful, but it’s not without obstacles. Here are a few common challenges and how to overcome them:
Lack of Buy-In
Operators may see QRQC as “just another meeting.” Make it meaningful by linking QRQC efforts to real results: less downtime, better product quality, fewer customer complaints.
Inconsistent Participation
If supervisors or team leads don’t consistently join QRQC routines, others will stop showing up too. Set the expectation that it is non-negotiable.
No Follow-Through
Identifying a problem is just the beginning. Without follow-through, teams will lose trust in the process. Assign ownership to every action and follow up during the next QRQC review.
The Role of Digital Tools in QRQC Implementation
Traditional QRQC boards rely on paper or whiteboards, but in modern manufacturing sites, digital tools offer a major advantage.
With a digital daily management system like fabriq, manufacturers can:
- Log problems in real time from any device
- Share updates across shifts and locations
- Track actions and owners automatically
- Visualize SQDIP metrics with live data
- Integrate problem-solving methods
Digital tools don’t just make QRQC easier, they make it more powerful. Teams gain visibility, accountability, and speed, without needing to rely on manual tracking or lost sticky notes.
If you’re already using some lean problem-solving techniques, a digital solution can help you scale what’s working.
Start Solving Problems in Real Time
Implementing QRQC doesn’t require a full lean transformation. Start small, stay consistent, and bring your teams into the process. The results of higher quality, faster decisions, and better teamwork will speak for themselves.
Are you ready to digitize your QRQC process? Request a demo of fabriq today. See how we can help you drive continuous improvement initiatives across your shopfloor.
